- architecture of controls
- creating a custom control.
- adding events handling to a control.
- stylling a control.
- source code.
- further reading.
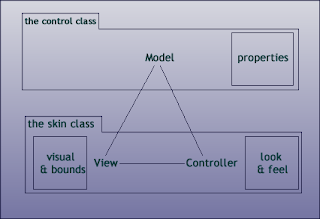
architecture of controls
all the controls extend the abstarct class Control which in turn extends the class Region. The Region class is a resizable Parent node which can be styled from CSS and also layout the children. the important properties and methods of the Region Class that you must take into account are the following :
| name | access | type | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| width | read-only | Double | the width of the node set by the parent container |
| height | read-only | Double | the height of the node set by the parent container |
| minWidth | read-write | Double | the overriden min max, preferred min, preffered and max for width and height of the Region |
| minHeight | read-write | Double | |
| prefWidth | read-write | Double | |
| prefHeight | read-write | Double | |
| maxWidth | read-write | Double | |
| maxHeight | read-write | Double | |
| padding | read-write | Insets | padding of the region |
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| computeMaxHeight(double width)
|
Computes the maximum height of this region. |
| computeMaxWidth(double width) | Computes the maximum width of this region. |
| computeMinHeight(double width) | Computes the minimum height of this region. |
| computeMinWidth(double width) | Computes the minimum width of this region. |
- padding is the space between the content and the content’s border.
- border is the line that’s drawn around each edge of the box.
- margin is what separates one node from another.
- the Inset is the sum of the padding and the border.
Controls follow the classic MVC design pattern. as you can see every Control (the model) has a reference to a single Skin. so there is a one to one relationship between them, The Control Class holds all the properties needed to represent his state and its the responsability of the Skin class to set the visual wich include calculating the min and max dimensions and handle all the interaction with the user.
creating a custom control.
so to implement a custom control we need two classes at leat one which extends the Control Class and one extends the skin Class. each of them have a methode that allow to retrieve the other.The skin of a control is defined by the Skin<C extends Skinnable> interface. this interface ha three methods :
custom control implementation will extend the Control class, and its skin implementation will extend the SkinBase class :
in our example the two classes are :
//the control :
public class LcdClock extends Control {
//....
@Override
protected Skin<?> createDefaultSkin() {
return new LcdClockSkin(this);
}
}
//the skin
public class LcdClockSkin extends SkinBase<LcdClock> {
//....
public LcdClockSkin(LcdClock control) {
super(control);
//....
}
the LcdClockSkin manage the properties of LcdClock and define its size by redefining these methods :
@Override
protected double computePrefHeight(double width, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return 100;
}
@Override
protected double computePrefWidth(double height, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return 300;
}
@Override
protected double computeMinHeight(double width, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return 30;
}
@Override
protected double computeMinWidth(double height, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return 100;
}
@Override
protected double computeMaxHeight(double width, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return computePrefHeight(width, topInset, rightInset, bottomInset, leftInset);
}
@Override
protected double computeMaxWidth(double height, double topInset, double rightInset, double bottomInset, double leftInset) {
return computePrefWidth(height, topInset, rightInset, bottomInset, leftInset);
}
the drawing of the clock is done by overrinding this method :@Override
protected void layoutChildren(double contentX, double contentY, double contentWidth, double contentHeight) {
if (invalidate){
updateClock(contentWidth, contentHeight) ;
invalidate=false;
}
layoutInArea(this.getNode(), contentX, contentY, contentWidth, contentHeight, -1, HPos.CENTER, VPos.CENTER);
}
adding event handling :
for demo purpose we add an onclick event to our control which print a simple message on the console :first of all we define an ordinary property : onActionPropriety. of the type EventHandler<ActionEvent>.
private final ObjectProperty<EventHandler<ActionEvent>> onAction = new ObjectPropertyBase<EventHandler<ActionEvent>>() {
@Override
public Object getBean() {
return LcdClock.this;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "onAction";
}
@Override
protected void invalidated() {
setEventHandler(ActionEvent.ACTION, get());
}
};
public EventHandler<ActionEvent> getOnAction() {
return onActionProperty().get();
}
public void setOnAction(EventHandler<ActionEvent> value) {
onAction.set(value);
}
public ObjectProperty<EventHandler<ActionEvent>> onActionProperty() {
return onAction;
}
after that we add the following code to the constructor of the skin Class :
getSkinnable().setOnMousePressed((e) -> {
getSkinnable().fireEvent(new ActionEvent());
});
skining the control :
Making a property styleable, then, consist of:- defining the javafx.beans.property as a StyleableProperty
- creating a corresponding CssMetaData
- ensuring the CssMetaData is returned in the List<CssMetaData>
in our case we are make only one property styleable. let's say it's the backgroundColor property. to achieve this result the property must extend one of the StyleableProperty classe. here the StyleableObjectProperty :
private ObjectProperty<Color> backgroundColor = new StyleableObjectProperty<Color>(Color.BLACK) {
@Override
public Object getBean() {
return LcdClock.this;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "backgroundColor";
}
@Override
public CssMetaData getCssMetaData() {
return StyleableProperties.LCD_CLOCK_METADATA;
}
@Override
public void invalidated() {
updateBackgroundColor();
}
};
In java doc we find the following definition of CssMetaData :
"A CssMetaData instance provides information about the CSS style and provides the hooks that allow CSS to set a property value. It encapsulates the CSS property name, the type into which the CSS value is converted, and the default value of the property.
CssMetaData is the bridge between a value that can be represented syntactically in a .css file, and a StyleableProperty. There is a one-to-one correspondence between a CssMetaData and a StyleableProperty. Typically, the CssMetaData of a will include the CssMetaData of its ancestors. During CSS processing, the CSS engine iterates over the Node's CssMetaData, looks up the parsed value of each, converts the parsed value, and sets the value on the StyleableProperty.
The method Node.getCssMetaData() is called to obtain the List<CssMetaData>. This method is called frequently and it is prudent to return a static list rather than creating the list on each call. By convention, node classes that have CssMetaData will implement a static method getClassCssMetaData() and it is customary to have getCssMetaData() simply return getClassCssMetaData(). The purpose of getClassCssMetaData() is to allow sub-classes to easily include the CssMetaData of some ancestor. "
"A CssMetaData instance provides information about the CSS style and provides the hooks that allow CSS to set a property value. It encapsulates the CSS property name, the type into which the CSS value is converted, and the default value of the property.
CssMetaData is the bridge between a value that can be represented syntactically in a .css file, and a StyleableProperty. There is a one-to-one correspondence between a CssMetaData and a StyleableProperty. Typically, the CssMetaData of a will include the CssMetaData of its ancestors. During CSS processing, the CSS engine iterates over the Node's CssMetaData, looks up the parsed value of each, converts the parsed value, and sets the value on the StyleableProperty.
The method Node.getCssMetaData() is called to obtain the List<CssMetaData>. This method is called frequently and it is prudent to return a static list rather than creating the list on each call. By convention, node classes that have CssMetaData will implement a static method getClassCssMetaData() and it is customary to have getCssMetaData() simply return getClassCssMetaData(). The purpose of getClassCssMetaData() is to allow sub-classes to easily include the CssMetaData of some ancestor. "
private static final CssMetaData<LcdClock, Color> LCD_CLOCK_METADATA = new CssMetaData<LcdClock, Color>("-fx-lcd-bk", StyleConverter.getColorConverter(), Color.BLACK) {
@Override
public boolean isSettable(LcdClock styleable) {
return styleable.backgroundColor == null || !styleable.backgroundColor.isBound();
}
@Override
public StyleableProperty<Color> getStyleableProperty(LcdClock styleable) {
return (StyleableProperty<Color>) (WritableValue<Color>) styleable.backgroundColor;
}
};
finnally getClassCssMetaData() and getCssMetaData() have to be created :
static {
List<CssMetaData<? extends Styleable, ?>> temp
= new ArrayList<>(Control.getClassCssMetaData());
Collections.addAll(temp, LCD_CLOCK_METADATA);
cssMetaDataList = Collections.unmodifiableList(temp);
}
private static final List<CssMetaData<? extends Styleable, ?>> cssMetaDataList;
@Override
protected List<CssMetaData<? extends Styleable, ?>> getControlCssMetaData() {
return getClassCssMetaData();
}
public static List<CssMetaData<? extends Styleable, ?>> getClassCssMetaData() {
return StyleableProperties.cssMetaDataList;
}
source code
you can find the source code for netbeans at https://github.com/mooninvader/lcdClock